Modern-day automobiles are truly an engineering marvel. They’re made up of complex systems and machinery that work in unison to achieve the perfect balance of efficiency, performance, and environmental friendliness.
Even though some enthusiasts dislike any mention of the latter, the fact remains that emissions control devices like the catalytic converter actually make our vehicles better.
Perhaps the most unglorified emissions control device is the EGR valve — hardly anyone ever talks about it. So that’s what we’re going to discuss in this guide.
Read on as we explore everything you need to know about faulty EGR valves along with preventative measures and quick fixes. Let’s dive right in.
What Is an EGR Valve? What Does It Do?
EGR stands for exhaust gas recirculation, and the EGR valve’s sole purpose is to recirculate a tiny proportion of the exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber.
This will sound counterintuitive at first but dig deeper and you’ll see just how fascinating this part actually is.

Here’s what happens (in a nutshell): the introduction of exhaust gasses back into the engine cylinder reduces the temperature in the engine cylinder.
With less oxygen and an altered chemical composition, the diluted air-fuel mixture burns slower and cooler, which allows it to curb NOx production.
This is crucial for emissions control because nitrogen oxides are the absolute worst pollutant that internal combustion engines produce, even more so than carbon monoxide.
To some people, this might come across as confusing because nearly 80% of the air we breathe is nitrogen and we literally need oxygen to survive. Why then, is the combination of the two harmful for us? It’s because of heat.
When nitrogen is exposed to the excessively high temperatures of the combustion chamber, the otherwise inert gas becomes reactive and creates NOx which then enters the exhaust stream.
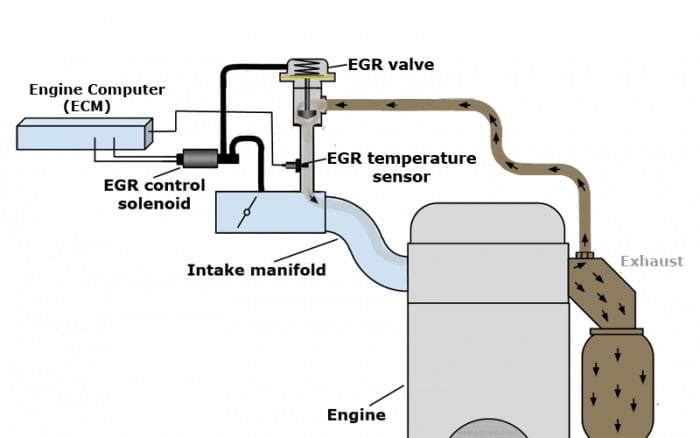
The EGR valve regulates the subsequent mixing of the exhaust gas with the intake air and channels a very metered proportion of the mixture back into the intake tract. That’s its primary purpose.
The secondary purpose is to reduce engine knocking. Read our guide to the best fuel octane boosters for more clarity.
As you may have guessed, if the EGR valve fails, your car won’t run correctly and you’ll experience a myriad of issues, which we will explain in this guide.
Bad EGR Valve Symptoms
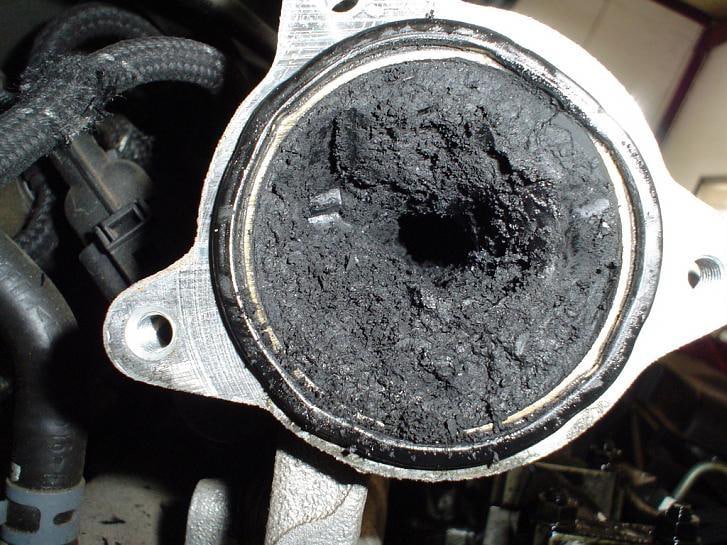

There are several tell-tale signs of a faulty EGR valve. To complicate things further, many of these signs also indicate other problems, so it is important to think about all the possibilities before concluding it is the EGR valve.
Below we’ve outlined some of the most common signs, what they look like, and how they might impact the drivability of your vehicle.
Rough Idle

Erratic and hesitant idling is an indicator that your EGR valve might be stuck open. When this happens, the valve pumps an unnecessarily large amount of exhaust gasses back into the engine cylinder.
As a result, this will decrease the volumetric efficiency of your engine, meaning, the air-fuel mixture won’t burn completely, which will sap some power.
Increased Fuel Consumption

If the EGR valve is stuck open, the combustion inside your engine cylinder will be incomplete and the air-fuel mixture won’t ignite efficiently. This means more fuel will be consumed when driving.
You might notice having to go to the gas station more often than usual. You can also rely on your car’s inbuilt MPG monitoring system to verify increased fuel consumption.
It is important to double-check your fuel consumption, regardless of how good or bad your fuel economy is in general.
Smelling Unburnt Fuel
Stuck-open EGR valves typically flood your engine cylinder with more fuel than what’s required, causing it to run too rich. This, combined with excess exhaust gas being recirculated into the engine means there’s going to be a lot of unburnt fuel.
This will cause more hydrocarbons to leave the tailpipe, so much so that your cabin might reek of unburned gasoline. Needless to say, this is really bad for your health.
It is important to note that smelling fuel can also indicate a leakage of some sort, and this is something you will want to have inspected and addressed as soon as possible to avoid expensive damage.
Engine Knocking
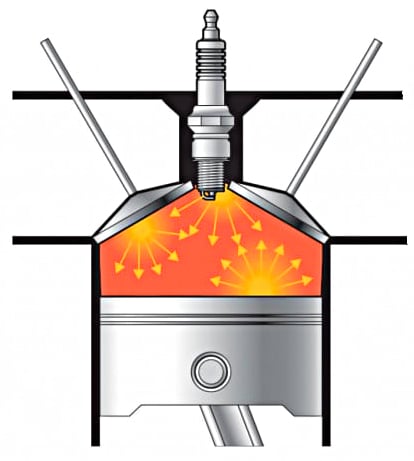
If the EGR valve remains closed, either because it is stuck or just does not open when it should, your engine will knock.
This is because the mixture in the combustion chamber will ignite early, also known as pre-ignition, as high temperatures will be reached faster without the exhaust gasses to help lower it.
Knocking can also be an indicator of other serious issues, but it may even happen because of something simple like poor fuel quality.
Check Engine Light

Faulty EGR sensors will typically trip the CEL. If you have a scan tool, you can check the codes yourself, otherwise, you can take it to most local service centers and they can run a scan for you.
A common Nissan OBD-II error code for a malfunctioning EGR valve is P0401. However, even if your car is not throwing this code, you might still have a bad EGR valve, so it is important to be thorough in addressing the signs.
EGR Valve: Clean or Replace?
If you’ve concluded that you have a bad EGR valve, you have two choices: clean it, or replace it.
The most likely reason your EGR valve is malfunctioning is because of carbon deposits, soot, and/or dirt buildup that leads to it being stuck closed or open. Simple cleaning usually resolves the problem.
However, if the valve is damaged physically, it’s advisable to just replace it. EGR valves are generally considered to have a 10-year lifespan. So if your valve is around or more than 10 years old, it’s about time you install a new one.

The DIY route is always cheaper and a lot more fun! However, if you’re not mechanically inclined, or if you simply prefer the convenience of having a trusted service center perform the work, then, by all means, get it done by a professional.
For those who do want to take the DIY route, we have some tips. To clean or replace an EGR valve, you need to uninstall it completely. Here’s how to fix it:
- Locate the valve. It is usually mounted on the intake manifold.
- Remove any connections to the valve. There might be electrical connectors or vacuum hoses. Be sure to inspect the hoses and/or connectors as well. If there appears to be any damage, they should be replaced and might even be the reason for the malfunctioning EGR valve.
- Remove all bolts holding the valve in place. There are normally a few bolts you can remove with a wrench or socket, effectively freeing the valve.
- Inspect the EGR valve’s gasket and replace it if damaged.
Clean an EGR Valve

Use a purpose-made EGR valve cleaner to safely and effectively remove buildup from the valve. After spraying the cleaner, use a brush or scraper to remove the deposits.
Sometimes, however, the buildup will not be so easy to remove. If this is the case, you can soak it in the cleaner for several minutes to agitate the gunk, then try to brush it off again. You might have to repeat this process a few times before the valve is clean.
EGR Valve Replacement
If replacing the EGR valve, follow the steps for removal, then do the same operations in reverse.
Be sure to inspect and replace any damaged connectors, hoses, or gaskets as needed, just like when cleaning the valve. Once this is done, you can mount the valve by tightening the bolts, and then reconnect any hoses or electrical connections.
Wondering how much it costs to replace an EGR valve? It ranges from $140 to $400, excluding labor. This of course depends on the car.
Fun fact: some JDM cars don’t even have an EGR valve — the Honda S2000 for instance! It’s likely the only Honda engine that doesn’t use one of these.
Types of EGR Valves
Older cars typically use vacuum-operated EGR valves, while modern vehicles all use electronically operated ones.
Different automakers implement the technology in different ways, but the main types of external EGR valves can be summarized as follows:
- Vacuum operated: This type of EGR valve uses a vacuum solenoid to open and close. It may also include a feedback sensor to keep the ECU informed about the valve’s position.
- Digital: The ECU plays a significant role in the operation of digital EGR valves. It involves a solenoid, a stepper motor, and a feedback sensor.
- Diesel high pressure: These EGR valves are designed to redirect the soot-containing exhaust gas to prevent it from entering the diesel particulate filter. The gas is then returned to the intake manifold via a network of pipes of galleys.
- Diesel low pressure: These valves redirect the exhaust gas after it passes through the DPF.
- Gasoline: Similar to the diesel high-pressure EGR valve, this one diverts exhaust gases into the combustion chamber. This happens because of the vacuum created by the piston; it draws the exhaust gases into the cylinder and the flow is regulated by the opening and closing of the EGR valve.
In Summary
Now that you know what the exhaust gas recirculation valve does, why it’s important, and what happens when it malfunctions, you’ll be able to diagnose this problem as soon as it arises.
The idea is to periodically clean your EGR valve so that it doesn’t get to a point where it stops working. We suggest stocking up on EGR valve cleaners, however, carb, brake, or mass airflow sensor cleaners will also do the job.
Would you rather clean your EGR valve yourself or let a professional mechanic take care of it? Let us know by leaving a comment below!


1 comment
Clean it myself! My mechanic wanted to charge me $750 to replace it. No thank you! Time to find a new mechanic!!!!