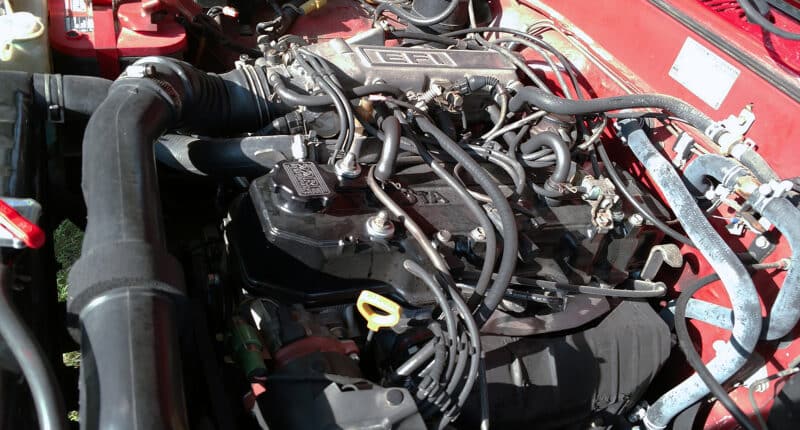
Toyota’s 22-R and 22-RE 4-bangers are old and aging motors compared to the K24s of today. As part of the R-series family, the 2.4L fuel-injected motors are as strong as they are reliable.
They’re not the most powerful motors right out of the box, but that’s something you can fix with a few mods. For engines that are from the mid-80s, the aftermarket support is pretty decent.
The durability of stock 22-RE and 22R engines is commendable, to say the least. Examples of these engines lasting over 400,000 miles with nothing but routine maintenance aren’t uncommon.
Join us as we take a closer look at the performance, specs, and reliability of Toyota’s 22-RE and 22R engines in this article.
Toyota 22-RE & 22R Engine Specs
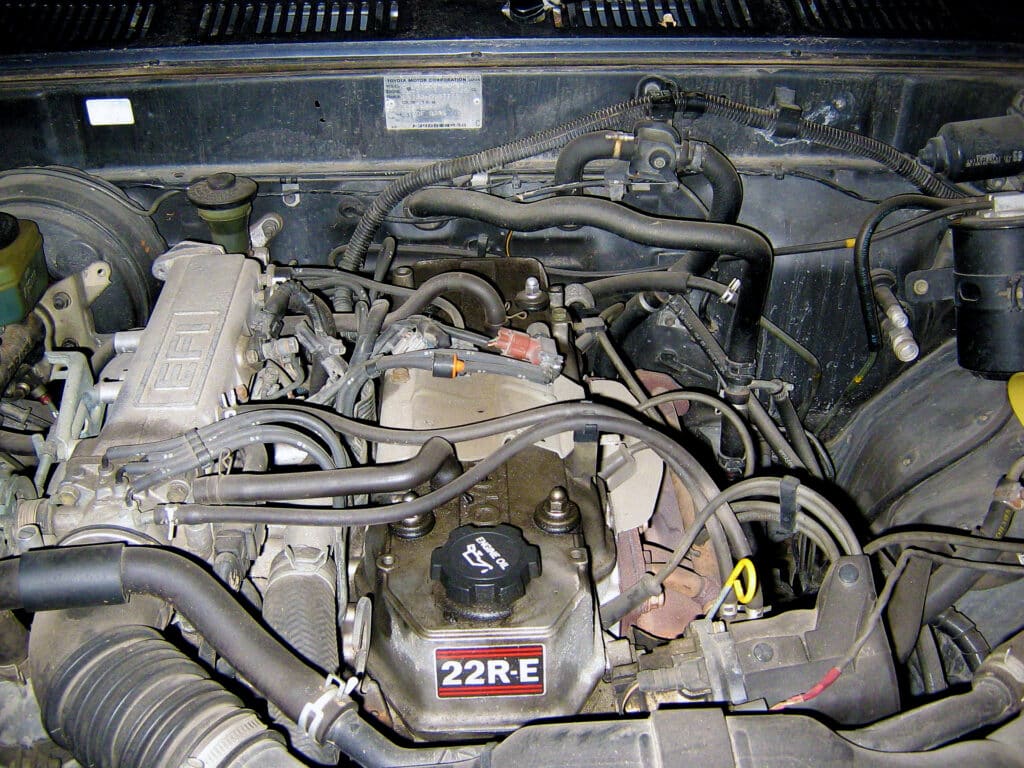

- Engine code: 22-RE, 22R
- Production: 1981-1997
- Layout: Inline-4 SOHC 8V (2 valves per cylinder)
- Displacement: 2.4L (2,366 cc)
- Fuel system: Electronic Fuel Injection, Carburetor (22R)
- Cylinder bore: 92 mm (3.62″)
- Piston stroke: 89 mm (3.5″)
- Compression ratio: 9.4:1
- Power: 105 to 113 hp (22-RE), 97 hp to 109 hp (22R)
- Torque: 136 lb-ft to 140 lb-ft (22-RE), 128 lb-ft to 138 lb-ft (22R)
- Firing order: 1-3-4-2
Being among the last members of Toyota’s R engine family, the 22R and 22-RE motors became popular choices for the JDM marque and found their way into a variety of tuner cars and trucks.
The 2.4L inline-4 engines started their life in 1981, specifically the 22R which was in production until 1997.
An improved version of the 22R, the 22-RE, was introduced in 1982. Both engines were heavily revised in 1985 and were in production until 1995 and 1997 respectively.
So much so that the post-1985 engines had very few interchangeable parts compared to earlier R engines.
The overhaul involved a revised cylinder head, block, pistons, and timing belts. Associated parts like the timing chain and water/oil pumps were also reworked in R motors produced after 1985.
All 22Rs and REs from 1985 and up are very similar, so you can consider the 22-RE as no more than a slightly advanced, fuel-injected version of the 22R.
With both motors, you get 2,366 cc to play with, and 2 valves per cylinder with a 92 mm bore and 89 mm stroke.
The compression ratio stands at 9.4:1 for EFi, with earlier 22-RE variants putting out 105 hp and 136 lb-ft of torque. Later models, introduced in 1985, were rated at 113 hp and 140 lb-ft.

The engines, like most JDM makes of the time, feature aluminum cylinder heads, while the blocks are made of cast iron.
But unlike some of the more popular JDM engines of the time, both R engines lacked a sporty edge, evident from their rather underwhelming power figures. In their defense, the engines were never designed to set lap times.
Although they lacked power, the 22R and 22-RE were well-known for their durability, fuel efficiency, and decent low-to-mid-range torque. Some of the cars featuring these engines include:
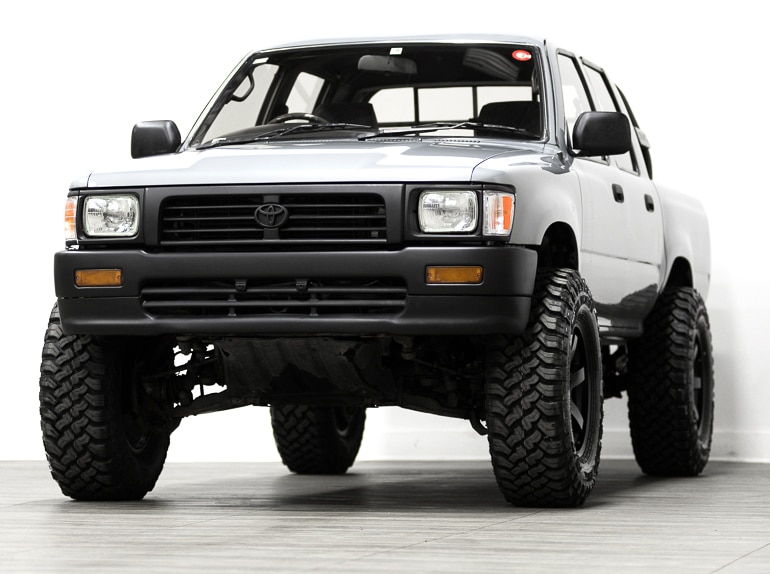
- 1984-1995 Toyota Hilux
- 1983-1985 Toyota Celica
- 1983-1987 Toyota Corona RT142
- 1984-1995 Toyota Pickup
- 1985-1995 Toyota 4Runner
- 1989-1997 Volkswagen Taro
How Long Do Toyota’s R Engines Last?
The cast-iron block lends these motors bulletproof reliability. Of course, it wasn’t just the engine block that helped. Everything from the soft piston rings to the overhead valvetrain design played a significant role in ensuring durability.
It’s not uncommon to see 22Rs and REs lasting over 400,000 miles. Accounts of the motors crossing 500,000 miles are available across multiple forums and internet discussions.
Plus, the engines are designed to be relaxed and under-stressed. Low output paired with over-engineered internals is usually considered an excellent combination, and Toyota’s R motors are a prime example of that.
While you may question their lack of power, the engines more than make up for it with their longevity and reliability.
But unfortunately, nothing’s perfect. R engine owners, especially post-1985 versions, have reported issues of a chattering sound emanating from the front of the engine.
The timing chain is stretched to a point where the tensioner cannot take up any more slack, causing it to rub against the chain guide and create noise.
The issue can snowball into more expensive repairs like damaged pistons, bent valves, and failed cooling systems if left unattended.
Can the 22R and 22-RE Handle Forced Induction?
Yes, they can. Toyota even developed a factory turbocharged version of the 22-RE, dubbed the 22-RTE.
It churns out 135 hp and 173 lb-ft of torque. Not the most exciting power figures in today’s motoring scene, but a sizable amount for a runabout in the late 80s.
So turbocharging is possible. However, the stock engine runs at a relatively high compression ratio, which is not advised for a forced induction setup.
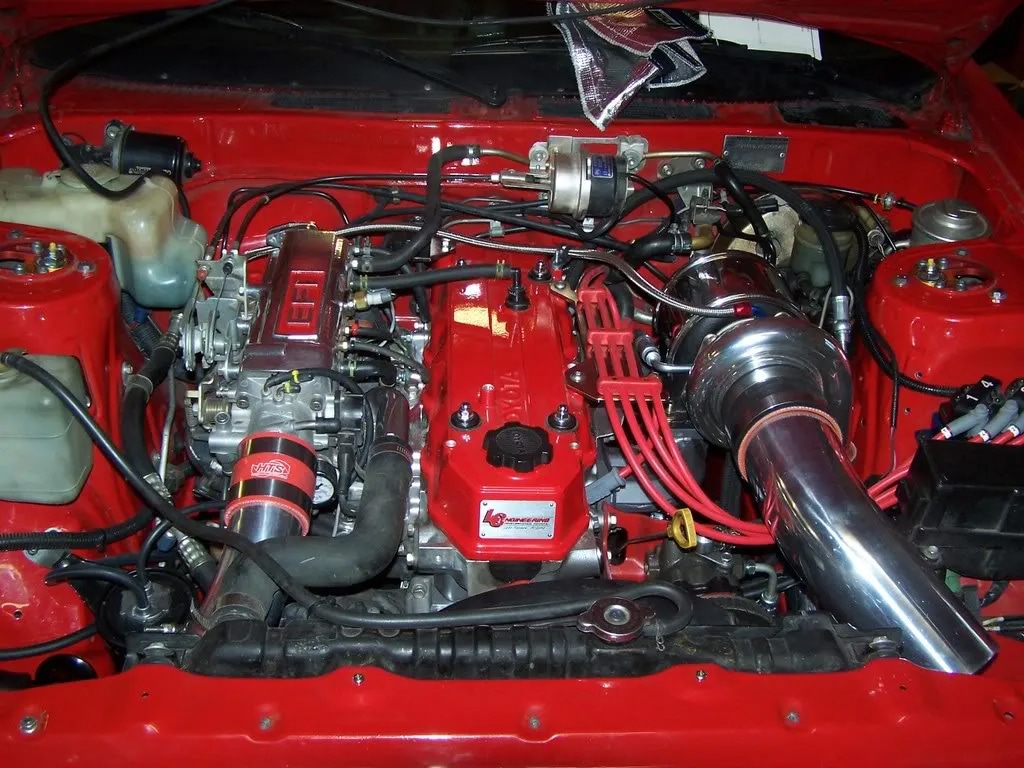

Ideally, you’d want to keep the boost pressure and compression low, as the stock ignition system is a bit sloppy and is not designed to retard timing to better optimize the additional air and fuel supply.
Anything below 8.5:1 and 7 PSI of boost is advised for pump gas.
Alternatively, you can upgrade the fuel injection system by installing bigger injectors. Pair that with forged internals, and you may reliably run a higher boost, unlocking more power.
Simple mods like an aftermarket exhaust manifold or headers, short ram or cold air intake, upgraded ignition system, and 22-RE performance cams should easily unlock around 120 whp.
Managing 300 hp from the 22-RE engine is possible by installing a forced-induction setup. But bear in mind that the engine is not exactly a rev-happy unit, owing to its large displacement and long block.
However, this can be remedied by installing a 20R head on the 22R block. The 20R has straight ports which means it will flow better, rev quicker, and significantly improve top-end performance. This is a simple bolt-on upgrade for pre-1985 22R engines.
It’s worth mentioning that this upgrade also requires the use of the 20R intake manifold, which introduces more complexities.
Concluding Summary
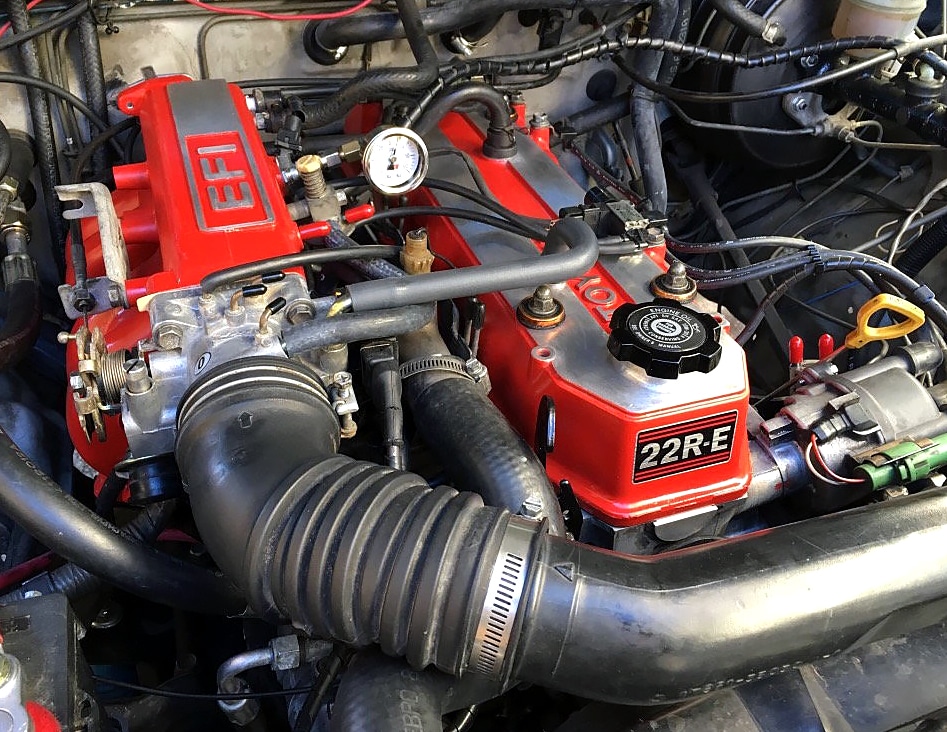

As you can tell, Toyota’s R engines are built to last. Sure, they may not be the most powerful or the most sophisticated engines out there, but they can outlive themselves while handling quite a bit of abuse.
A textbook example of reliability, the 22R and RE, in addition to being durable, are also excellent platforms for mods. They’re among the most reliable Toyota engines ever made.
The engines aren’t too complicated, yet they feature robust internals, a cast-iron block, and 2.4 liters of displacement. Although they’re outdated, they’re by no means fragile.
Install some tastefully selected upgrades and they’ll be almost as good, if not better, than most 3-cylinder hoovers you find in modern runabouts.
How many miles do you have on your R motor? Let us know by leaving a comment below! If you find this post helpful, consider sharing it with your friends on Facebook, Reddit, and your favorite car forums. We appreciate your support!

